AbstractIntroduction: "Idiopathic" ventricular arrhythmias most often arise from the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT), although arrhythmias from the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) are also observed. While previous work has elucidated the mechanism and electropharmacologic profile of RVOT arrhythmias, it is unclear whether those from the LVOT share these properties. The purpose of this study was to characterize the electropharmacologic properties of RVOT and LVOT arrhythmias. |
AbstractMối liên quan giữa biến cố mạch vành cấp tính và phản ứng dị ứng đã được công nhân trong nhiều năm. Trường hợp đầu tiên được báo cáo vào năm 1950, trong một phản ứng dị ứng với penicillin. Năm 1991, Kounis và Zavras mô tả hội chứng đau thắt ngực do dị ứng và dị ứng gây nhồi máu cơ tim, hiện nay được gọi là hội chứng Kounis. Có 2 loại được mô tả: loại I, xảy ra ở những bệnh nhân không có các tổn thương thực thể động mạch vành và được gây ra bởi sự co thắt động mạch vành, và loại II, xảy ra ở bệnh nhân có thương thực thể mạch vàkhi các sự kiện dị ứng gây ra xói mòn mảng bám hoặc làm vỡ các mãng xơ vữa. Hội chứng này đã được báo cáo gắn với một loạt các yếu tố tiếp xúc với môi trường, và tiếp xúc với thuốc. Trong bài này, chúng tôi thảo luận về các bệnh lý, các yếu tố gây dị ứng, các triệu chứng liên quan, và điều trị hội chứng Kounis. Braunwald lưu ý rằng đau thắt ngực vasospastic có thể được gây ra bởi các phản ứng dị ứng, với các trung gian như histamin và leukotrienes tác động lên cơ trơn mạch máu vành. [8,9] do đó, đau thắt ngực dị ứng và dị ứng nhồi máu cơ tim đã trở thành công nhận là hội chứng Kounis. [6,7] Hội chứng Kounis (KS), hoặc sự đồng thuận của biến cố mạch vành cấp tính với các phản ứng dị ứng hoặc quá mẫn, đã ngày càng được báo cáo trong y văn. Tần suất thực sự của KS là không rõ. Tuy nhiên, trong một nghiên cứu nọc độc của côn trùng thách thức chẩn đoán Brown và cộng sự báo cáo rằng 9,5% tình nguyện khỏe mạnh phát triển đau ngực bất thường trên điện tâm đồ phù hợp với thiếu máu cục bộ cơ tim cấp tính. [10] Classification an ... Read more » |
|
DR. Babacon
A Look at RVOT VTThe following images were collected from one procedure. The images selected provide some valuable insight to RVOT arrhythmias. To the right of each image is an explanation of what the image displays and what role the information displayed plays in the overall procedure. Note that the first image is a standard surface 12 lead recording. When ectopy presents itself at the start of any procedure, it is important to record a 12 lead. Many times it is difficult to reproduce focal arrhythmias in the lab once a patient is supine or sedated. If you have a 12 lead recording based upon the lead placement within the lab, then you can always resort to pacemapping if the rhyth ... Read more » Attachments:
Image 1
|
AbstractThe prevalence of coronary artery disease in female patients is increasing due to changing lifestyle patterns including cigarette smoking, diabetes and stress. Since women are delaying childbearing until older age, acute coronary syndrome will more frequently occur during pregnancy. Although rare, acute coronary syndrome during pregnancy often has devastating consequences. It is associated with increased maternal and neonatal mortality and morbidity compared with the nonpregnant situation. Furthermore, it constitutes an important problem for the patient and the treating physician, because the selection of diagnostic and therapeutic approaches is greatly influenced not only by maternal, but also by fetal safety.
IntroductionCoronary heart disease is a major health problem. Although rare in pregnant women, during pregnancy acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is estimated to occur three- to four-times more often compared with the nonpregnant women in this age group. ... Read more » |
|
A total of 23 patients that underwent CA (40%) had no ECG confounders (ECG is "otherwise unremarkable”). LMCA disease was found in only 3 of them (13%), LMEQ in 2 (9%) and three vessel disease in 5 (22%). The prevalence of three vessel disease, LMCA or LMEQ was 43%, not different from that of the whole group. A total of 16 patients (70%) underwent revascularization with 30% undergoing PCI and 43% CABG. Most of the patients that underwent CA had positive T waves (53 patients). Among the 4 patients with negative T waves, one had three vessel disease, one LMCA and two nonsignificant coronary artery disease (Table 4). Among the 57 patients that underwent CA, 25 (44%) had dynamic ECG changes and in 17 patient ... Read more » |
MethodsWe collected 142 electrocardiograms (ECGs) with dates ranging from March 2, 2008 to April, 13 2011 from the ones sent for routine reading at the St. Luke's Episcopal Hospital ECG laboratory and read by one investigator (YB). ECGs showing diffuse ST segment depression in > 7 leads with ST-segment elevation in aVR were collected. Patients with left bundle branch block, QRS duration of > 130 msec, ventricular rhythm or ventricular paced rhythm were excluded. The polarity of the T waves in the leads with maximal ST depression was defined as positive if the terminal part of the T wave was > 0.1 mV above the isoelectric line, or negative. Demographic data, date of ECG, the indication for the ECG, presence of elevated cardiac markers, diagnosis of cardiac conditions (non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome [NSTE-ACS], non-ischemic dilated car ... Read more » |
|
|
|
|
|
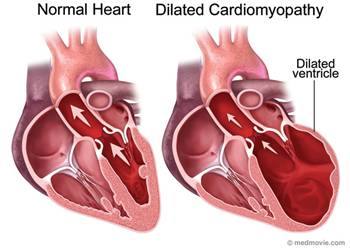
Dilated cardiomyopathy or DCM is a condition in which the heart becomes weakened and enlarged and cannot pump blood efficiently. The decreased heart function can affect the lungs, liver, and other body systems.
|
|
WARREN ISAKOW, MD
Respiratory failure is a common reason for intensive care unit admisson and is the final pathway for a number of disease of differing pathophysiology. an mechanism-based approach enables the clinician to identify the most likely cause for the respiratory failure and to treat appropriately. In general, patients with respiratory failure may be classified into groups, depending on the component of the respiratory system that is involved. Hypercapnic respiratory failure is a consequence of ventilatory failure and is recognized by an elevated PaCO2 above normal (>45mmHg at sea level). This denotes failure of the respiratory pump an can occur with normal lungs. Hypoxemic respiratory failure is a consequence of gas exchange failure and is recognized by hypoxemia ( PaO2 < 60mmHg ) with or without widening of the alveolararterial O2 gradient. HYPERCAPNIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE The hallmark of hypercapnic respiratory failure is an elevated PaCO2 above 45mmHg. &nb ... Read more » |
BackgroundIdiopathic ventricular tachycardia in patients with an anatomically
normal heart is a distinct entity whose management and prognosis differs
from ventricular tachycardia associated with structural heart disease. |
|
Mặc dù hóa trị liệu là một biện pháp hiệu quả trong điều trị căn bệnh
ung thư. Tuy nhiên, bên cạnh khả năng tiêu diệt tế bào ung thư thì hóa
trị cũng tác động đến các tế bào khỏe mạnh và tạo ra tác dụng phụ như
buồn nôn, nhiễm độc gan, gây tổn hại hệ miễn dịch. Vì vậy, để hóa trị
liệu trở nên an toàn hơn, các nhà nghiên cứu đến từ đại học Tel Aviv
(TAU) đã chế tạo một phương tiện phân phối thuốc trực tiếp đến các tế
bào ung thư trước khi các chất hóa học ảnh hưởng đến tế bào xung quanh.
Thiết bị có kích cỡ nano được tiến sĩ Dan Peer và giáo sư Rimona Margalt phát triển. Như đã nói ở trên, thiết bị cho phép phân phát lượng thuốc điều trị trực tiếp đến các tế bào ung thư, tránh tác động đến các tế bào khỏe mạnh từ đó tăng hiệu quả chữa trị mà không gây tác dụng phụ. Tiến sĩ Peer cho biết: "Thiết bị rất giống một quả bom chùm." Bên trong thiết bị là các hạt thuốc siêu nhỏ. Khi thiết bị tiếp xúc với tế bào ung thư, chúng lập tức "nhả" các chất hóa học vào tế bào. Theo tiến sĩ Peer, thiết bị phân phối này có thể được sử dụng để chữa trị nhiều loại ung thư khác nhau bao gồm ung thư máu, phổi, ruột, ung thư vú, buồng trứng, ung thư tụy và đặc biệt là ung thư não. Chìa khóa thành công của thiết bị chính là phần tử cấu tạo vỏ ngoài - một loại đường được thụ thể trên nhiều chủng tế bào ung thư tiếp nhận. "Khi thiết bị tác động đến một thụ thể trên tế bào ung thư, thụ thể sẽ bị thay đổi cấu trúc. Sau đó, dược chất được phát tán trực tiếp vào tế bào ung thư và tập trung tiêu diệt các tế bào gây bệnh này," tiến sĩ Peer giải thích. Do thiết bị chỉ phản ứng với các tế bào ung thư, các tế bào khỏe mạnh xung quanh vẫn không bị ảnh hưởng. Ngoài ra, thiết bị được chế tạo từ các vật liệu hữu cơ. Vì vậy, ... Read more » |
|
TS. Đỗ Thị Minh Thìn 1. Đại cương. 1.1. Giải phẫu tuyến thượng thận: 1.2. Sinh lý tuyến thượng thận: + Sinh lý vỏ th ... Read more » |
|
I. ĐẠI CƯƠNG:
1. Khái niệm: Bệnh tê phù còn có tên bệnh Beriberi. Chỉ một bệnh cảnh lâm sàng: mệt mỏi các cơ bắp, các chi có cảm giác tê tê, bì bì phản xạ gân xương giảm hoặc mất kèm theo phù nề mặt trước xương chầy. Cũng có khi biểu hiện suy tim, đau bụng cấp, hôn mê. Bệnh có thể xảy ra lẻ tẻ một vài người nhưng cũng có thể thành vụ dịch lớn. Bệnh có thể qua khỏi nhanh khi được dùng Vitamin B1 ngay với liều cao, nhưng cũng có thể tử vong mà không cứu chữa kịp. Bệnh khá phổ biến trong quân đội. 2. Điều kiện sinh bệnh: - Gặp ở những nước có tập quán ăn gạo (gạo giã kỹ quá, gạo máy, gạo mốc, gạo hẩm, gạo vo kỹ quá). + Châu Á: Trung Quốc, Nhật Bản, Việt Nam... + Châu Phi: Togô, Cameroun... + Châu Mỹ: Brasil, Cu Ba... - Chế độ ăn thiếu rau tươi hoặc dùng nhiều loại rau chứa ít Vit.B1. - Khí hậu quá nóng, quá lạnh thay đổi đột ngột. Ở Việt Nam bệnh tê phù thường xảy ra vào mùa hè (Đ.V.Chung 1977) vì: + Nóng cơ thể dùng nhiều Vit.B1 hơn ... Read more » |
|
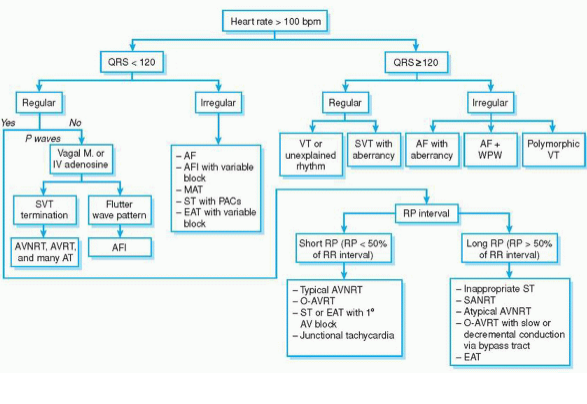
1. Triệu chứng:
- Cơn xảy ra đột ngột, bệnh nhân cảm thấy tim đập nhanh, bồn chồn, hồi hộp, có thể chóng mặt, buồn nôn, khó thở, tức ngực. - Mạch quay khó bắt, tần số 150 – 180 ck/phút hoặc hơn, đều. Cơn có thể kéo dài vài giây, vài phút hay vài giờ, hiếm gặp kéo dài hơn và kết thúc cũng đột ngột. - Ghi điện tâm đồ trong cơn: nhịp nhanh đều, các phức bộ QRS đều, sóng P thường không nhìn thấy vì nhịp quá nhanh, đoạn ST hạ thấp. 2.Xử trí: - Làm lần lượt các biện pháp sau để kích thích dây X cho đến khi thấy có hiệu quả: . Nuốt một miếng bánh. . Hít vào, thở ra mạnh. - Ngồi gấp mình ra trước, đầu cúi vào giữa hai gối. . Nghiệm pháp Valsalva: bệnh nhân thở ra hết - hít vào thật sâu - nhịn hơi rồi rặn thở. Làm 3 - 4 lần không kết qủa ngưng. . Xoa xoang cảnh: làm từng bên 10 - 20 giây, làm lại vài lần nếu không thấy có tụt huyết áp, doạ ngất (không được xoa cả 2 bên một lần). < ... Read more » |